Thin-Film Solar Panels: Everything to Know
Solar power has become an increasingly popular choice for residential and commercial properties as people become more aware of the need for renewable energy sources. One type of solar panel that has gained attention in recent years is thin-film solar panels. These panels are lightweight, flexible, and have a unique appearance compared to traditional solar panels. In this article, we'll explore what thin-film solar panels are, how they work, and their advantages and disadvantages. We'll also compare them to monocrystalline solar panels, the most common type of solar panel on the market.
Let's dive in!
How Thin-Film Solar Cells Are Made
Thin-film solar panels are made by depositing a thin layer of semiconductor material onto a substrate, such as glass or plastic. The semiconductor material is then patterned to create a series of interconnected cells that generate electricity when exposed to sunlight.
Comparison of the Four Main Types of Thin-Film Solar Panels
When considering thin-film solar panels, it's important to understand the differences between the four main types of cells. Here's a comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of each type:
Amorphous silicon (a-Si) solar cells:
Advantages: low cost, flexible, can perform well in low light conditions
Disadvantages: lower efficiency than other types, less durable, may degrade over time
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) solar cells:
Advantages: high efficiency, low cost, performs well in high temperatures
Disadvantages: less durable, may release toxic materials during manufacturing, limited availability
Copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS) solar cells:
Advantages: high efficiency, flexible, performs well in low light conditions
Disadvantages: more expensive than other types, may degrade over time, complex manufacturing process
Organic photovoltaic (OPV) cells:
Advantages: low cost, flexible, lightweight
Disadvantages: lower efficiency than other types, less durable, may degrade over time
Overall, the best type of thin-film solar panel for you will depend on your specific needs and circumstances. If you're looking for a budget-friendly option, a-Si or OPV cells might be the way to go. If you prioritize efficiency and withstanding high temperatures, CdTe cells might be the best choice. CIGS cells offer a good balance of efficiency and flexibility but are more expensive.
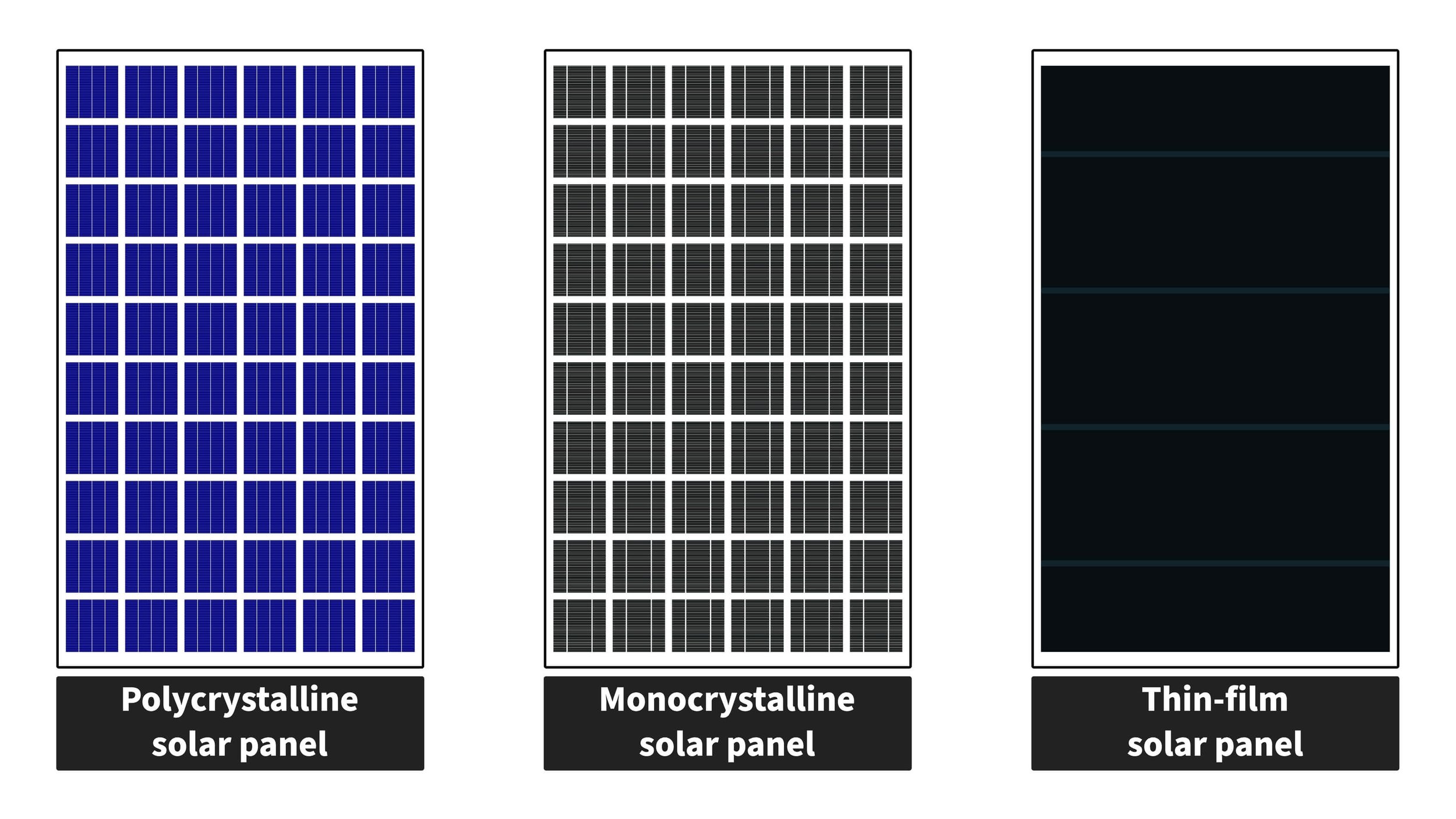
What Do Thin-Film Solar Panels Look Like?
Thin-film solar panels have a distinctive appearance compared to traditional crystalline solar panels. Rather than having a uniform grid of solar cells, thin-film solar panels have a smooth surface that is often colored in a dark blue or black. This uniform surface is due to the manufacturing process, which involves depositing a thin layer of semiconductor material onto a substrate.
The appearance of thin-film solar panels has both benefits and drawbacks. On the positive side, the uniform surface allows for a sleek and modern design that can be more visually appealing to some people. Thin-film solar panels can also be more flexible than traditional crystalline solar panels, allowing them to be integrated into a wider variety of surfaces, such as curved or irregular shapes.
On the negative side, the uniform surface can also make thin-film solar panels more noticeable on a roof or other surface. Some people may prefer the less noticeable appearance of traditional solar panels, which can be integrated into a grid-like pattern that blends into the roof or surface. Additionally, the uniform surface of thin-film solar panels can be more prone to shading, as any shadow on the surface can reduce the output of the entire panel.
Thin-Film Solar Panels vs. Monocrystalline Solar Panels
When it comes to solar panels, there are two main types: thin-film solar panels and monocrystalline solar panels. Monocrystalline solar panels are made from a single, large silicon crystal and are known for their high efficiency and durability. Thin-film solar panels, on the other hand, are made by depositing a thin layer of photovoltaic material onto a substrate such as glass or metal. Here are some key differences between the two types of solar panels:
Efficiency: Monocrystalline solar panels are typically more efficient than thin-film solar panels. This means they can generate more electricity per square foot of panel surface area. However, this difference in efficiency is becoming smaller as thin-film solar technology improves.
Durability: Monocrystalline solar panels are known for their durability and can last up to 25 years or more. Thin-film solar panels, on the other hand, have a shorter lifespan and may need to be replaced more frequently.
Cost: Thin-film solar panels are generally less expensive than monocrystalline solar panels, making them a more affordable option for homeowners and businesses. However, the cost of solar panels can vary depending on the manufacturer and other factors.
Appearance: Thin-film solar panels have a unique appearance compared to monocrystalline solar panels, which have a uniform, dark blue or black color. Thin-film solar panels can come in a variety of colors and designs, making them a popular choice for architects and designers.
Overall, choosing between thin-film solar panels and monocrystalline solar panels will depend on individual preferences, budget, and other factors such as efficiency and durability requirements. In the next section, we'll explore the pros and cons of thin-film solar panels in more detail.
The Efficiency of Thin-Film Solar Panels
One of the main considerations when choosing a solar panel is its efficiency, or how effectively it converts sunlight into electricity. Thin-film solar panels generally have lower efficiency compared to traditional monocrystalline solar panels, but there are additional factors to consider.
Compared to monocrystalline solar panels, thin-film solar panels typically have lower efficiency ratings. Monocrystalline solar panels have an average efficiency rating of around 22%, while thin-film solar panels have an efficiency rating of around 11-13%. However, it's important to note that the difference in efficiency may not be significant enough to outweigh the other benefits of thin-film solar panels, such as their flexibility and low cost.
The efficiency of thin-film solar panels can also be affected by a variety of factors, such as temperature, shading, and the angle of the panels relative to the sun. In general, thin-film solar panels tend to perform better in low-light conditions, but may not perform as well in high temperatures or when shaded.
It's also worth noting that while thin-film solar panels may have lower efficiency ratings, they can still be a viable option for many residential and commercial applications. By installing more panels to compensate for the lower efficiency, or by choosing a more efficient type of thin-film solar panel, it's possible to achieve the same level of electricity generation as with traditional solar panels. Ultimately, the decision to choose thin-film solar panels over traditional solar panels will depend on the specific needs and constraints of the project, as well as the budget and preferences of the homeowner or business owner.
Elevated Temperatures and Thin-Film Solar Panels
One important consideration when choosing solar panels is how they perform in high-temperature environments. Thin-film solar panels can be affected by high temperatures, but they also have some advantages in these conditions.
When thin-film solar panels are exposed to high temperatures, their efficiency can decrease. This is because the heat can cause the electrons in the solar cells to become more agitated and move around more quickly, which can decrease the electrical output of the panel. However, this effect can be mitigated by choosing a type of thin-film solar panel that is designed to perform well in high-temperature environments.
On the other hand, one advantage of thin-film solar panels in high-temperature environments is their flexibility. Because they are made with flexible materials, thin-film solar panels can be installed on curved or irregular surfaces, which can be beneficial in hot climates where traditional rigid solar panels may be less effective.
Another advantage of thin-film solar panels in high-temperature environments is their lower sensitivity to shading. In hot climates, shading can be a significant issue for traditional solar panels, as even partial shading can significantly decrease the output of the panel. However, thin-film solar panels are less affected by shading, which can make them a good option in areas with high levels of shading.
In summary, while thin-film solar panels can be affected by high temperatures, they also have some advantages in these conditions, such as flexibility and lower sensitivity to shading. By choosing a type of thin-film solar panel that is designed to perform well in high-temperature environments, it's possible to minimize the negative effects of elevated temperatures and take advantage of the benefits of thin-film solar panels.
The lifespan of Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels typically have a shorter lifespan compared to monocrystalline solar panels. The average lifespan of a thin-film solar panel is around 10 to 15 years, while monocrystalline solar panels can last up to 25 years or more. However, the lifespan of a thin-film solar panel can vary depending on several factors.
Factors affecting the lifespan of thin-film solar panels include the quality of materials used in their manufacturing, the specific type of thin-film solar panel, the conditions in which they are installed, and the level of maintenance they receive. Proper installation and regular maintenance can significantly extend the lifespan of thin-film solar panels.
It's important to note that the lifespan of a thin-film solar panel does not necessarily dictate its usefulness. Even after the end of its lifespan, a thin-film solar panel may still produce electricity, albeit at a reduced rate. Therefore, it's important to consider the potential return on investment when deciding whether or not to install thin-film solar panels.
Price of Thin-Film Solar Panels
The price of thin-film solar panels is typically lower than that of monocrystalline solar panels. The cost of thin-film solar panels can range from $0.50 to $0.80 per watt, while monocrystalline solar panels can cost $0.70 to $1.20 per watt. The exact price of thin-film solar panels can vary depending on several factors, such as the manufacturer, the specific type of thin-film solar panel, and the quantity purchased.
Despite the lower initial cost, it's important to consider the potential return on investment when deciding between thin-film and monocrystalline solar panels. While thin-film solar panels may be less expensive upfront, they typically have a shorter lifespan and lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline solar panels. This means that, over time, the cost savings may be offset by lower energy production and the need for more frequent replacements.
In addition to the cost of the panels themselves, it's important to factor in the cost of installation, which can vary depending on the complexity of the installation, the location of the property, and local labor costs. Many solar panel companies offer financing options and incentives that can help make the installation costs more manageable for homeowners and businesses.
FAQ
-
Thin-film solar panels can be a good choice for residential use, especially if you have limited roof space or are looking for a more flexible design. However, they may not be as efficient as traditional solar panels, so it's important to consider your energy needs and budget when deciding which type of solar panel to use.
-
Choosing whether or not to use thin-film solar panels depends on your specific energy needs, budget, and installation requirements. Consult a professional solar installer like ESS Solar to determine the best solar panel option for your home or business.
-
Yes, but we do NOT recommend it!
Conclusion
In conclusion, thin-film solar panels offer a promising alternative to traditional solar panels, with their lightweight design, flexibility, and lower cost. While they may not be as efficient as traditional solar panels, they can be a good choice for residential use, especially in areas with limited roof space. As technology advances, we can expect to see even more innovations in the renewable energy industry, and thin-film solar panels will undoubtedly play a role in shaping the future of solar power.