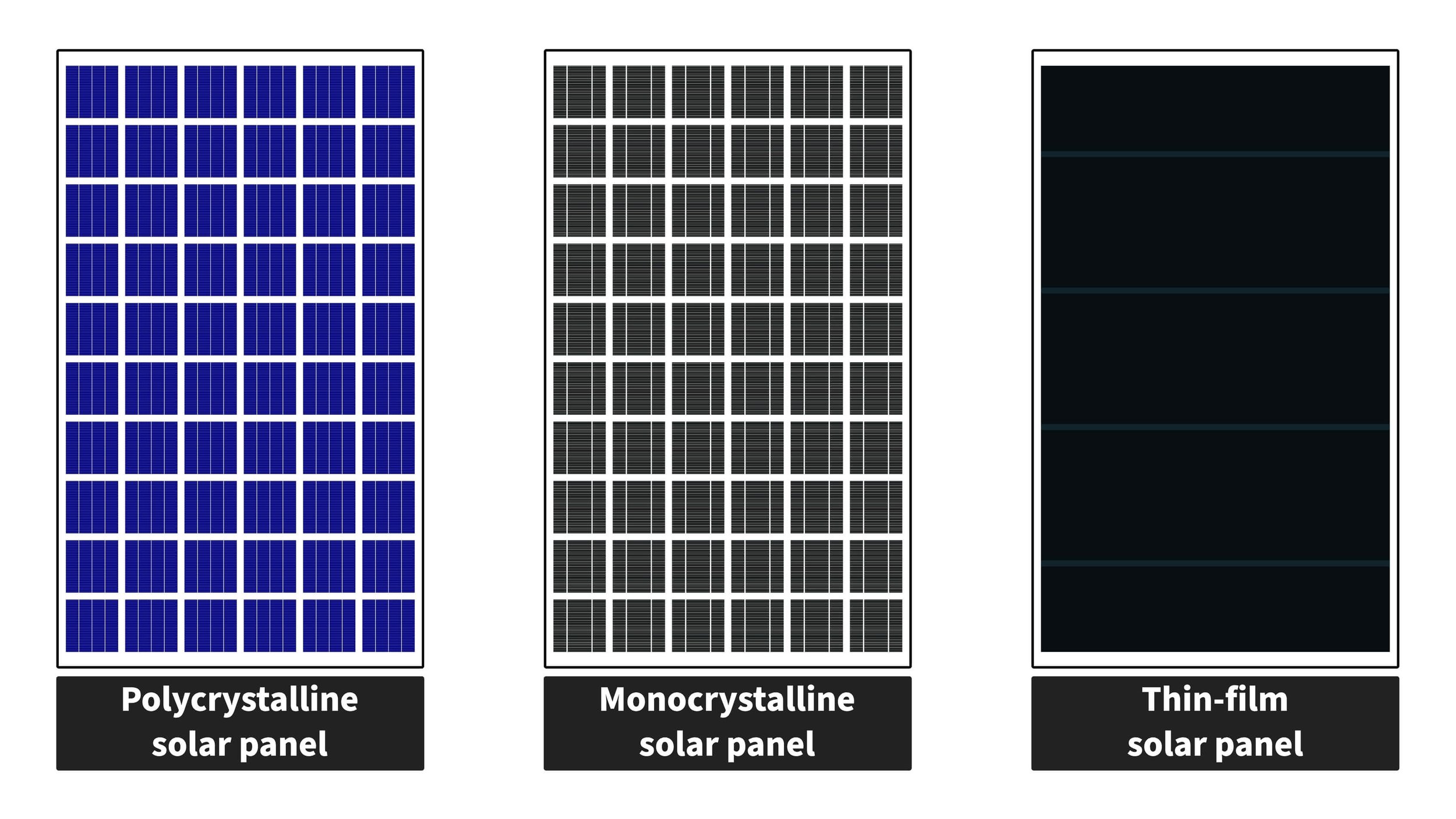
Polycrystalline VS Monocrystalline VS Thin Film
Introduction
Solar energy is no longer a thing of the future; it's here and now. With a plethora of options available, choosing the right solar panel can be overwhelming. In this ultimate guide, we'll dive deep into the world of solar panels, comparing Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin Film technologies. Let's get started!
Table of Contents
What are Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin Film Solar Panels?
Key Metrics Comparison
Advantages and Disadvantages
Other Factors to Consider
FAQ
Conclusion
What are Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin Film Solar Panels?
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Made from a single, high-purity silicon crystal, Monocrystalline panels are the epitome of efficiency. They're sleek, black, and built to last.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Polycrystalline panels are the budget-friendly cousins of Monocrystalline panels. They're made from multiple, smaller silicon crystals and have a blue, speckled appearance.
Thin Film Solar Panels
The new kids on the block, Thin Film panels are made by depositing a thin layer of semiconductor material onto a substrate like glass or plastic. They're flexible, lightweight, and come in various colors.
Key Metrics Comparison
Cost
Monocrystalline: Expensive
Polycrystalline: Budget-friendly
Thin Film: Most affordable
Efficiency
Monocrystalline: High (around 22%)
Polycrystalline: Moderate (15-17%)
Thin Film: Lower (11-13%)
Lifespan
Monocrystalline: 25-30 years
Polycrystalline: 25-30 years
Thin Film: 10-15 years
Aesthetics
Monocrystalline: Sleek, black
Polycrystalline: Blue, speckled
Thin Film: Various colors, smooth surface
Advantages and Disadvantages
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Advantages
High efficiency
Long lifespan
Aesthetically pleasing
Disadvantages
Expensive
Less efficient at higher temperatures
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
Advantages
Cost-effective
Tolerant to partial shading
Disadvantages
Lower efficiency
Less aesthetically pleasing
Thin Film Solar Panels
Advantages
Affordable
Flexible design
Performs well in high temperatures
Disadvantages
Lower efficiency
Shorter lifespan
Other Factors to Consider
Temperature Coefficient
Monocrystalline panels have a lower temperature coefficient, meaning they perform better in hot conditions compared to Polycrystalline panels.
Flexibility
Thin Film panels can be installed on curved or irregular surfaces, making them versatile for unique architectural designs.
Shading Tolerance
Polycrystalline and Thin Film panels are more tolerant to shading compared to Monocrystalline panels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
Yes, solar cell technology is constantly improving. New materials and manufacturing techniques are being developed to increase efficiency and decrease costs.
-
Yes, it is possible to use both polycrystalline and monocrystalline solar cells simultaneously. However, it is important that the voltage and current output of each panel are compatible with each other and with the rest of the system.
-
The most effective type of solar panel depends on the specific needs of the user. Monocrystalline panels tend to be more efficient, but they also come at a higher cost. Polycrystalline panels are more affordable and may be a better choice for those with limited space. Other types of solar panels, such as thin-film solar panels, PERC cells, and bifacial solar panels, offer their unique benefits and maybe a better choice depending on the user's specific needs.
-
Yes, especially if you have limited roof space or unique architectural features.
-
Consider factors like budget, space, and local climate conditions.
-
Generally, no. Always consult the manufacturer's guidelines.
Conclusion
Choosing between Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin Film solar panels boils down to your specific needs, aesthetic preferences, and budget. Each type has its pros and cons, but all contribute to a more sustainable future. So, do your research, consult with experts, and make an informed decision. After all, the sun is for everyone!